Mud leg provides hydrostatic pressure in order to prevent mud going through the separator into the rig. If the pressure in the mud gas separator exceeds hydrostatic pressure provided by mud leg, gas blowing through situation will be happened. Once blow-through occurs with a mud gas separator, it is very difficult to stop this situation until the mud leg column is re-established.

Figure 1 illustrates mud-blow through. The pressure that will create blow-through can be calculated by determining hydrostatic pressure of mud leg.
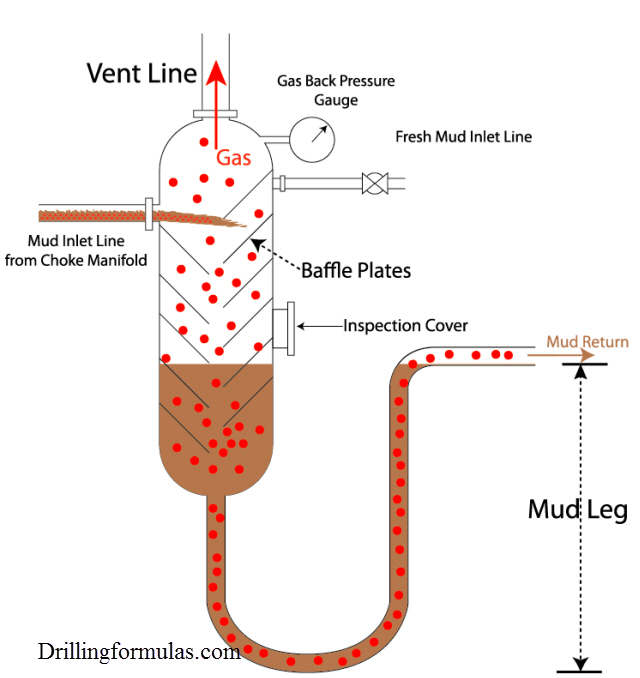
Figure 1 – Blow Through Situation
The equation below demonstrate the blow-through pressure.
Hydrostatic Pressure from Mud Leg = 0.052 × Mud Weight× Mud Leg
Where;
Hydrostatic Pressure from Mud Leg in psi
Mud Weight in ppg
Mud Leg in ft
Use the following data to calculate which pressure would blow-through occur.
Mud Leg = 20 ft
Mud Density in a mud gas separator = 13.0 ppg
Vent line length = 150 ft
Mud gas separator height = 25 ft
Solution
Only mud leg and mud density will be used in the calculation.

Figure 2 – Mud Gas Separator Information
Hydrostatic Pressure from Mud Leg = 0.052 × 13.0 × 20
Hydrostatic Pressure from Mud Leg = 13.5 psi
It means that if it is required 13.5 psi in this mud gas separator to overcome the hydrostatic pressure and gas blow-through will be occurred.
Reference books:  Well Control Books
Well Control Books