This is the brief explanation of a Kelly rotating system on the rig. Kelly rig is on an old style rigs and nowadays it is mostly used on land operations. For offshore operation, a top drive system is used instead.
First of all, it is important for new people to look at these images before reading the information below because they show the equipment’s name and where they are on the rig.
(Ref Inage: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/face/images/03ok034c.jpg)

(Ref Image: http://geologie.vsb.cz/DRILLING/drilling/theory/theory_html_m61697c8b.jpg)

(Ref Image: http://ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu/212_spring2011.web.dir/Dan_Luo/picture/hoisting.png)
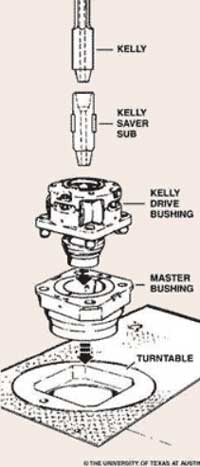
The upper end of the drill pipe is screwed onto the saver sub. The saver sub is used to protect and minimize wearr and tear on the threads at the bottom of the Kelly. The Kelly is about 40 ft in length with a square or hexagonal shape and it is hollow throughout in order to transport the drilling mud. Kelly moves freely through a Kelly bushing even though the drill stem is rotated.
A Kelly cock valve is located at the top of a Kelly and it is a safety valve which can be closed to stop back pressure from coming back to damage other surface equipment.
A swivel attached to the hook does not rotate, but at the bottom part it supports the Kelly which is being rotated while drilling. Drilling mud is pumped from a mud pump to a stand pipe manifold, Kelly hose and then to a gooseneck connection at a swivel.
A rotary table rotates a Kelly bushing and it simultaneously rotates a Kelly and a drill string and a drill bit. A rotary table has two main functions. The first one is to provide rotation to a drill stem and a bit and the second function is to hold slip in order to support the weight of a drill stem when it is not connected to a Kelly.
Generally, a rotary drive consists of a chain and rotary-drive sprocket. A rotary-drive sprocket is a part of the draw-works. In other rig power systems, an independent electric motor or engine with a direct drive to a rotary table is utilized. For this case, the rotary is normally driven by a drive shaft instead of a chain and rotary-drive sprocket.
A master bushing severs its function as a rotary motion transmission from a rotary table to a Kelly. Additionally, it is a link between a slip and a rotary table.
A Kelly bushing (some people call “rotary Kelly bushing”) engages a master bushing via four pins and rollers inside a Kelly bushing to allow a Kelly to move up or down freely while it is rotated or in a static mode.
This video demonstrates how to make a connection via a Kelly system.