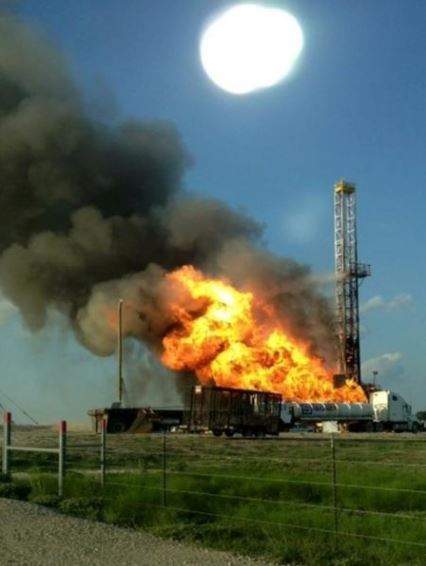
Many people tend to confuse between possible and positive well control indicators therefore we would like to differentiate between these two well control indicators.
![What-are-differences-between-possible-and-positive-well-control-indicators]()
Possible Well Control (kick) Indications
Possible well control (kick) indicators mean that there is possibility to get influx into wellbore. It MAY or MAY NOT be a kick.The indications can be either kick or just formation react while drilling. You need to remember that just only a single possible indicator cannot may not good enough to identify underbalanced condition in wellbore and the possible kick indicators must be used collectively. Therefore, drilling team on the rig needs to closely monitor the well and prepare appropriate action plans.
The possible well control (kick) indications are as follows;
Change in drilling breaks (ROP change) – If the differential between formation pressure and hydrostatic pressure created by drilling mud decreases, there is possibility to increase rate of penetration because the hold down effect is decreased.
Increase drag and torque – Increasing in drilling torque and drag are usually noticed while drilling into overpressured shale formation because underbalanc hydrostatic pressure exerted by drilling fluid column cannot to hold back the formation intrusion into wellbore. Shale normally has low permeability so formation fluid will not come into wellbore. Anyway, if we drill ahead pass high shale pressure into overpressured high permeability zones such as sand or carbonate, the formation fluid will flow into wellbore resulting in kick. This is very important to record frequently drilling torque and drag because it could be your well control indicator.
Decrease in Shale Density – Typically, shale density will increase as we drill deeper. If we see decrease in shale density, it may indicate that your well is in underbalance condition because high pressure zones (abnormal pressure) develop within large shale section. Practically, density of shale must be measured frequency and plot against drilling depth. You can see from a chart if there is any deviation in trend that could be an indication of change in pore pressure.
Increase in cutting size and shape – Pieces of formation may break apart and fall into wellbore because of underbalance situation. Because rocks pieces broken by underbalance condition are not ruined by bit, they will be more angular and bigger than normal cutting. Larger of cutting size will be result in difficulty to circulate them out of wellbore, hence, there will be more hole fill and torque and drag will increase. In addition, without a proportional increase in ROP (rate of penetration), cutting volume coming over shale shakers will increased noticeably.
Decrease in d-Exponent Value - Normally, trends of d-Exponent will increase as we drill deeper, but this value will decrease to lower values than what we expect in transition zones. By closely monitored d-Exponent, d-Exponent chart will be useful for people on the rig to notify the high pressure transition zones.
Read and understand about d-Exponent and learn how to calculate d-Exponent and normalized d-Exponent (corrected d-Exponent)
Change in Mud property- Without any chemical added into drilling fluid system, its property change due to increasing in water and/or chloride content indicates that formation fluid enters into the wellbore.
For some drilling mud, when salt water enters into the wellbore and mix with drilling fluid, the mud viscosity will increase.
In water base mud with low Ph salt saturated, the mud viscosity will decrease because of water from formation mixing with mud.On the other hand, water contamination in oil base mud will result in viscosity increases.
Increase in Temperature from Returning Mud - By observing trend of temperature coming from mud return, temperature trend showing deviation from the normal temperature trend can be an indication of abnormal pressure zones, especially while drilling into transition zones.
There are some factors that you need to account for when you try to evaluate mud temperature changes as listed below;
- Surface temperature conditions
- Elapsed time since tripping
- Mud chemicals used
- Wellbore geometry
- Circulating rate
- Cooling effect when drilling fluid flows through a long riser (deep water consideration)
Increase in trip, connection and/or background gas – Gas in mud, normally called gas cut mud, does not be a sign of a well flowing because it could be gas coming from formation. Nonetheless, personnel on the rig should keep in mind as a possible kick indicator. Hence, flow show and PVT (pit volume total) must be closely monitored.
Gas in the mud can come from one or more of the reasons listed below:
- Drill into a formation that contains gas or hydrocarbon.
- Temporally reduce in hydrostatic pressure due to swabbing effect.
- Pore pressure in a formation is greater than the hydrostatic pressure provided by drilling fluid in a wellbore.
Positive Well Control (kick) Indications
Positive well control (wellbore influx) indications mean indications showing almost 100% kick (wellbore influx) into wellbore. We can classify the positive indicators the following categories.
Positive Well Control Indicators While drilling
Increase in flow show – Without any increasing in flow rate in, increase in return flow indicates something coming into wellbore while drilling. Therefore, flow show instrument provided by the rigs or service companies must be checked and calibrated frequently.
Increase of active pit system (Pit gain) - Because drilling fluid system on the rig is a closed system, increasing in flow show without adjusting flow rate in will cause pit gain in a pit system. Nowadays, with high technology sensors, detecting change in pit level is easily accomplished at the rig site. However, visually check the pit level is importance as well for double checking figure from the sensors. Sometimes, change in pit level may be detected after the increase in flow show because it takes more time to accumulate volume enough to be able to detect by pit sensors.
Continue flowing while the pumps are off – When pumps are turned off, bottom hole pressure will decrease due to loss of equivalent circulating density (ECD). If there is any flow coming after pumps off, it indicates formation influx into wellbore.
Positive Kick Indicators While Tripping
Trip log deviation such as short fill up while tripping out and excess pit gain while tripping in. For tripping operation, it is very important to have a filling system via trip tank that provides continuous hole fill all time. With utilizing that system, we can compare fluid that is filled in or returned from wellbore with steel volume of tubular (drill pipe, drill collar, BHA, tubing, casing, etc). If drilling fluid volume is less than theoretical pipe displacement while tripping out or more return fluid while running in, you need to flow check and monitor the well.
• If flow check indicates wellbore influx, crew must quickly shut the well in.
• If flow check does not show any influx, drill string must be run back to bottom in order to circulate at least bottom up to ensure hole condition.
Positive flow when pipe is static. Every time that pipe in static condition. Trip tank with correct filling system must be monitored all time by both rig personnel and mud logger. If volume in trip tank increases, personnel must confirm flow check and prepare to shut the well in.
We wish this article will clear your mind about the possible and positive well control indicators.
Reference book: ![well-control-book]() Well Control Books
Well Control Books
Recap from the following articles: http://www.drillingformulas.com/positive-kick-wellbore-influx-indications/
http://www.drillingformulas.com/possible-kick-wellbore-influx-indications-part1/
http://www.drillingformulas.com/possible-kick-wellbore-influx-indications-part2/
 Please leave us a good feedback if you like our book.
Please leave us a good feedback if you like our book.




























































 Drilling Hydraulic Books
Drilling Hydraulic Books


 Well Control Books
Well Control Books
















 Oilfield Resume
Oilfield Resume Successful Oilfield Interviews
Successful Oilfield Interviews




 Drilling Fluids, Mud Pumps, and Conditioning Equipment Book
Drilling Fluids, Mud Pumps, and Conditioning Equipment Book








